Low-Voltage Internet Wiring: Step-by-Step Installation Tips
Low-Voltage Internet Wiring: Step-by-Step Installation Tips
Ever feel like your internet is stuck in the slow lane, even though you're paying for premium speeds? Or maybe you're dreaming of a smart home but dread the thought of tangled wires? The solution might be simpler than you think: strategic low-voltage internet wiring.
Low-voltage wiring is the backbone of modern connectivity, powering everything from your internet router and security cameras to smart thermostats and landscape lighting. Understanding how to properly install and manage this wiring is crucial for reliable performance, enhanced safety, and future-proofing your home or business. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, providing step-by-step instructions and essential safety advice to ensure a smooth and successful installation.
Understanding Low-Voltage Wiring for Internet and Beyond
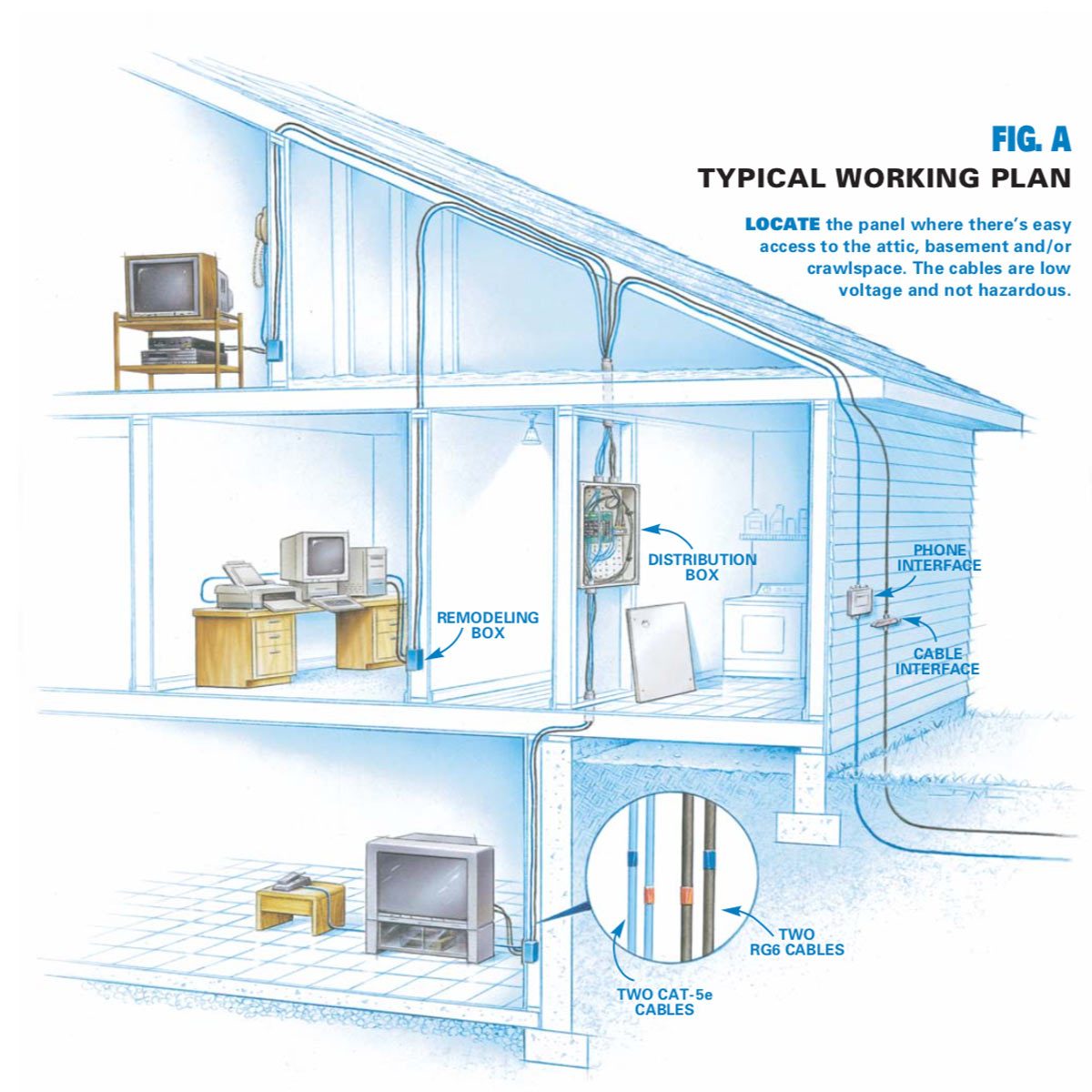
Low-voltage wiring, typically ranging from 50 to 1000 volts AC or 75 to 1500 volts DC, is designed to carry signals and power for various applications. In the context of internet and smart home systems, it commonly involves Cat5e, Cat6, or coaxial cables for data transmission, and lower voltage wires for powering devices like security cameras, smart doorbells, and access points. Unlike high-voltage electrical wiring, low-voltage wiring poses a lower risk of electric shock but still requires careful handling and adherence to safety guidelines.
Why is Proper Low-Voltage Wiring Important? Reliable Performance: Properly installed and terminated cables ensure optimal signal strength and minimal data loss, resulting in faster and more consistent internet speeds. Scalability and Future-Proofing: Structured cabling allows you to easily add or modify network connections as your needs evolve, accommodating new devices and technologies. Improved Aesthetics: Neat and organized wiring improves the overall appearance of your home or business, preventing unsightly cable clutter. Enhanced Safety: Correct wiring practices minimize the risk of electrical hazards and potential damage to your equipment. Increased Home Value: A well-wired home with modern networking infrastructure is a desirable feature for potential buyers.
Essential Tools and Materials
Before you start any wiring project, gather the necessary tools and materials. Having everything on hand will save you time and frustration.
Cable Tester: Verifies the integrity of your cable connections. Crimper: Used to attach RJ45 connectors to Ethernet cables or F-connectors to coaxial cables. Wire Stripper: Removes the outer jacket of cables without damaging the inner wires. Punch Down Tool: Inserts wires into terminal blocks on patch panels or wall jacks. Fish Tape or Wire Puller: Helps to run cables through walls or conduits. Drill with various drill bits: For creating pilot holes and mounting hardware. Screwdrivers (Phillips and Flathead): For securing screws and fasteners. Voltage Tester (Non-Contact): Detects the presence of voltage in existing wiring.CRITICAL for safety. Safety Glasses: Protect your eyes from debris. Gloves: Provide grip and protect your hands. Cat5e/Cat6 Cable: For Ethernet connections. Choose the appropriate length and category based on your needs. Coaxial Cable: For connecting to cable internet or antennas. RJ45 Connectors: For terminating Ethernet cables. F-Connectors: For terminating coaxial cables. Wall Plates and Jacks: Provide a clean and professional finish for your wiring. Patch Panel (Optional): Centralizes network connections in a structured cabling system. Cable Ties or Velcro Straps: Organize and manage cables. Conduit (Optional): Protects cables running through walls or ceilings. Label Maker: For identifying cables and connections.
Step-by-Step Guide to Low-Voltage Network Wiring
This section outlines the general steps involved in installing low-voltage internet wiring. Remember to consult local building codes and regulations before starting any project. When in doubt, hire a qualified electrician.
Step 1: Planning and Design Assess Your Needs: Determine the number of network connections you need and their locations. Consider future expansion possibilities. Create a Wiring Diagram: Map out the cable routes and termination points. This will help you estimate the amount of cable required and identify any potential obstacles. Choose Cable Pathways: Decide how you will run the cables (e.g., through walls, ceilings, conduits). Consider accessibility and aesthetics.
Step 2: Safety First – Power Down! Turn off the power: Always turn off the power to any circuits you will be working near. Use a non-contact voltage tester to ensure the power is off. This isabsolutely crucial to avoid electrical shock.
Step 3: Running the Cables Drill Pilot Holes: If running cables through walls or ceilings, drill pilot holes for the cables. Be careful not to drill through existing wiring or plumbing. Use Fish Tape or Wire Puller: Attach the cable to the fish tape or wire puller and carefully pull it through the wall or conduit. Avoid Sharp Bends: Avoid sharp bends in the cable, as this can damage the conductors and affect signal quality. Secure Cables:Secure the cables to walls or ceilings using cable ties or staples. Avoid pinching the cables.
Step 4: Terminating the Cables Strip the Outer Jacket: Use a wire stripper to carefully remove the outer jacket of the cable, exposing the inner wires. Be careful not to nick or damage the inner wires. Arrange the Wires: Arrange the wires according to the T568A or T568B wiring standard (be consistent throughout your installation). These standards define the color order of the wires in the RJ45 connector. Insert Wires into RJ45 Connector: Carefully insert the wires into the RJ45 connector, ensuring that each wire is fully seated. Crimp the Connector: Use a crimper to crimp the connector onto the cable. Test the Connection: Use a cable tester to verify that the connection is working properly.
Step 5: Installing Wall Plates and Jacks Mount the Wall Plate: Secure the wall plate to the wall using screws. Connect the Cable to the Jack: Connect the cable to the jack, following the wiring diagram. Snap the Jack into the Wall Plate: Snap the jack into the wall plate.
Step 6: Testing and Labeling Test All Connections: Use a cable tester to verify that all connections are working properly. Label Cables:Label each cable at both ends to identify its purpose and location. This will make it easier to troubleshoot problems in the future.
Tips for Effective Cable Management
Effective cable management is essential for maintaining a clean, organized, and functional wiring system.
Use Cable Ties or Velcro Straps: Bundle cables together using cable ties or Velcro straps to prevent tangling and clutter. Route Cables Strategically: Plan your cable routes carefully to minimize the amount of visible wiring. Conceal Cables: Use cable concealers or raceways to hide cables running along walls or floors. Use a Patch Panel: A patch panel centralizes network connections and makes it easier to manage and troubleshoot your wiring. Label Everything: Label all cables and connections clearly and accurately. Maintain Adequate Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation around network equipment to prevent overheating. Avoid Overcrowding: Don't overcrowd cables in conduits or raceways. Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to identify and address any potential problems, such as loose connections or damaged cables.
Wiring Troubleshooting: Common Issues and Solutions
Even with careful planning and installation, you may encounter issues with your low-voltage wiring. Here are some common problems and their solutions: Slow Internet Speed:
Cause: Damaged cable, loose connection, outdated equipment, incorrect wiring.
Solution: Check cables for damage, tighten connections, upgrade equipment, verify wiring standards (T568A/B). Use a cable tester to verify the integrity of the cable run. Intermittent Connection:
Cause: Loose connection, interference, faulty equipment.
Solution: Tighten connections, move cables away from sources of interference (e.g., power cords), replace faulty equipment. No Connection:
Cause: Broken cable, disconnected cable, faulty equipment.
Solution: Check cables for breaks, ensure cables are properly connected, test equipment with known working cables. Signal Degradation:
Cause: Long cable runs, sharp bends in cable, interference.
Solution: Use shorter cable runs, avoid sharp bends, shield cables from interference.
If you're unsure about troubleshooting, it's best to call a qualified electrician or network technician.
Smart Home Wiring Considerations
Planning for a smart home requires foresight and careful consideration of your future needs.
Centralized Wiring Panel: Consider using a centralized wiring panel to manage all your smart home wiring. Dedicated Circuits: Install dedicated circuits for smart home devices that require a lot of power. Future-Proofing: Install extra cables to accommodate future smart home devices. Wireless Access Points: Strategically place wireless access points to ensure strong Wi-Fi coverage throughout your home. Security System Wiring: Plan for security system wiring, including cameras, sensors, and alarms. Home Automation Wiring: Consider wiring for home automation systems, such as lighting control, temperature control, and entertainment systems. Low Voltage Lighting:Plan your landscape lighting or indoor accent lighting, and pre-wire for these systems before walls are closed.
Safety Precautions: Protecting Yourself and Your Home
Working with electrical wiring, even low-voltage, requires caution. Follow these safety precautions to protect yourself and your home: Always Disconnect Power: Always disconnect power to the circuit before working on any wiring. Use a Voltage Tester: Use a non-contact voltage tester to ensure the power is off. Wear Safety Glasses: Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from debris. Use Insulated Tools: Use insulated tools to prevent electrical shock. Follow Building Codes: Adhere to all local building codes and regulations. Don't Overload Circuits: Don't overload circuits with too many devices. Inspect Wiring Regularly: Inspect wiring regularly for damage or wear. If in Doubt, Call a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of the wiring process, call a qualified electrician.
People Also Ask
Can I run low voltage and high voltage wiring together?
No, it is generally not recommended to run low-voltage and high-voltage wiring in the same conduit or bundle. High-voltage wiring can induce interference in low-voltage wiring, affecting performance. Additionally, mixing these types of wiring can create a safety hazard. Always keep them separate and follow local electrical codes.
What is the best type of cable for internet wiring?
For most home and small business internet wiring needs, Cat6 cable is a great choice. It supports Gigabit Ethernet speeds and is backward compatible with older standards like Cat5e. For higher bandwidth applications or future-proofing, consider Cat6A.
How do I troubleshoot a slow internet connection after installing new wiring?
First, double-check all your connections to ensure they're properly seated and crimped. Use a cable tester to verify the integrity of each cable run. Also, make sure your network devices (router, modem, etc.) are functioning correctly. If the problem persists, it might be related to your internet service provider (ISP).
Conclusion
Installing low-voltage network wiring may seem daunting at first, but with careful planning, the right tools, and adherence to safety guidelines, it's a manageable DIY project. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a reliable and efficient network infrastructure that meets your current and future needs. Remember to prioritize safety, test your connections thoroughly, and label everything clearly. A well-wired home or business is a smart investment that will enhance your connectivity, improve your productivity, and increase the value of your property. So, grab your tools, roll up your sleeves, and get ready to experience the benefits of a properly wired network!
Posting Komentar untuk "Low-Voltage Internet Wiring: Step-by-Step Installation Tips"